🧠 What Is a Motherboard?
A motherboard, also known as a mainboard or system board, is the primary printed circuit board (PCB) in a computer. It serves as the central hub that connects and allows communication between all hardware components, including the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and peripherals.
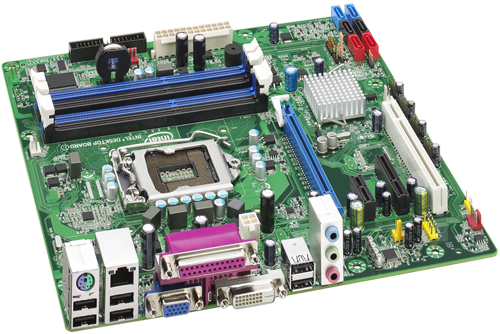
⚙️ Functions of a Motherboard
- Central Hub: Facilitates communication between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and peripherals.
- Power Distribution: Distributes power from the power supply to various components.
- Data Communication: Manages data transfer between components via buses and chipsets.
- Peripheral Connectivity: Provides ports and slots for external devices and expansion cards.
- System Management: Hosts the BIOS/UEFI firmware for system initialization and configuration.
🧩 Types of Motherboards
Motherboards vary based on form factor, chipset, and intended use:
- Form Factor:
- ATX: Standard size, commonly used in desktop PCs.
- Micro ATX: Smaller than ATX, offers fewer expansion slots.
- Mini ITX: Compact size, suitable for small form factor builds.
- Chipset:
- Determines compatibility with CPUs, memory, and expansion cards.
- Examples include Intel Z-series and AMD B-series chipsets.
- Intended Use:
- Consumer: General-purpose motherboards for everyday computing.
- Gaming: Enhanced features for high-performance gaming.
- Workstation: Designed for professional applications requiring high reliability.
- Server: Optimized for data centers and enterprise environments.


🧩 Parts of a Motherboard and Their Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| CPU Socket | Houses the processor; types include LGA (Intel) and PGA (AMD). |
| RAM Slots | Accommodate memory modules (DIMMs); typically 2–4 slots. |
| PCIe Slots | Allow expansion cards like GPUs, sound cards, and network cards. |
| Chipset | Manages data flow between the processor, memory, and peripherals. |
| Power Connectors | Supply power to the motherboard and connected components. |
| Storage Connectors | Interface for storage devices; includes SATA and M.2 slots. |
| I/O Ports | Provide external connectivity; includes USB, audio, and network ports. |
| CMOS Battery | Powers the BIOS settings and system clock when the PC is off. |
🏭 How Are Motherboards Manufactured?
Motherboard manufacturing involves several key steps:
- Design: Engineers create the motherboard layout, specifying component placement and electrical pathways.
- PCB Fabrication: The design is transferred onto a multi-layer PCB using photolithography and etching processes.
- Component Placement: Automated machines place surface-mount components onto the PCB.
- Soldering: Components are soldered onto the PCB using reflow soldering techniques.
- Testing: The assembled motherboard undergoes functional testing to ensure quality and performance.
- Packaging: After passing tests, motherboards are packaged and prepared for shipment.
🌍 Where Are Motherboards Manufactured?
Leading motherboard manufacturers and their production locations include:
- ASUS: Production facilities in Thailand, Vietnam, and Indonesia. (Tom’s Hardware)
- ASRock: Manufacturing in Taiwan and China.
- Gigabyte Technology: Facilities in Taiwan and China.
- MSI (Micro-Star International): Production in Taiwan and China.
- Intel: Manufactures server motherboards in the United States.
🛒 How to Select a Motherboard
Consider the following factors when choosing a motherboard:
- CPU Compatibility: Ensure the motherboard’s socket type matches your processor (e.g., LGA1700 for Intel 12th/13th Gen).
- Chipset Features: Select a chipset that supports your desired features, such as overclocking or multiple M.2 slots.
- Form Factor: Choose a size that fits your case and meets your expansion needs.
- RAM Support: Verify the motherboard supports the amount and speed of RAM you plan to use.
- Expansion Slots and Ports: Ensure adequate PCIe slots, USB ports, and storage connectors.
- Budget: Balance features with cost to find the best value.
🧪 How to Check a Motherboard
To test a motherboard:
- Visual Inspection: Check for visible damage, such as burnt areas or damaged capacitors.
- POST Test: Connect the motherboard to a power supply, CPU, RAM, and speaker.
- If the motherboard beeps, it indicates the CPU and RAM are functioning.
- No beeps may suggest a problem with the motherboard or components.
- Component Testing: Test individual components (CPU, RAM, PSU) on a known working motherboard to rule out faulty parts.
🛠️ How to Fit a Motherboard
- Prepare the Case: Install the I/O shield into the case.
- Align the Motherboard: Place the motherboard into the case, aligning the I/O ports with the I/O shield.
- Secure the Motherboard: Screw the motherboard into the standoffs in the case to prevent short circuits.
- Connect Components: Attach the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and power connectors.
❌ How to Remove a Motherboard
- Power Down: Turn off the system and disconnect all cables.
- Remove Components: Disconnect and remove the CPU, RAM, and expansion cards.
- Unscrew the Motherboard: Remove screws securing the motherboard to the case.
- Extract the Motherboard: Carefully lift the motherboard out of the case.
🛍️ How to Buy a Motherboard
When purchasing a motherboard:
- Online Retailers: Websites like Amazon, Newegg, and Flipkart offer a wide selection.
- Local Computer Stores: Visit local retailers for hands-on assistance and immediate availability.
- Manufacturer Websites: Buy directly from manufacturers like ASUS, MSI, or Gigabyte for the latest models.
For a visual understanding of motherboard components and their functions, you might find this video helpful:
FAQs About Motherboard
💻 What Is a Motherboard in a Computer?
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in a computer.
It serves as the central hub that connects all internal components, such as the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and expansion cards, allowing them to communicate and function together. (techtarget.com)
🧾 What Is the Motherboard Short Answer?
The motherboard is the primary circuit board in a computer that houses and interconnects all essential components, enabling the system to operate cohesively. (techtarget.com)
🧬 Why Is It Called a Motherboard?
The term “motherboard” originates from its role as the main circuit board in a computer, serving as the foundation for all other components.
It can be extended by plugging other circuit boards into it, known as daughterboards. (english.stackexchange.com)
🧩 How Many Parts Are in a Motherboard?
A motherboard comprises several key components, including:
- CPU Socket: Houses the processor.
- RAM Slots: Accommodate memory modules.
- Chipset: Manages data flow between the CPU, memory, and peripherals.
- Expansion Slots (PCIe/PCI): Allow additional cards like graphics or sound cards.
- Power Connectors: Distribute power to the motherboard and connected components.
- Storage Connectors: Interface with storage devices like HDDs or SSDs.
- I/O Ports: Provide external connectivity options.
- BIOS/UEFI Chip: Stores firmware for system initialization.
- CMOS Battery: Maintains BIOS settings when the system is powered off.
🧭 What Is the Northbridge and Southbridge?
In traditional motherboard architecture:
- Northbridge: Handles high-speed communication between the CPU, RAM, and graphics card.
- Southbridge: Manages slower peripheral interfaces like USB, audio, and storage devices. (geeksforgeeks.org)
Modern systems have integrated these functions into a single chipset, often referred to as the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). (reddit.com)
🔌 What Is a CPU Socket?
A CPU socket is a physical interface on the motherboard that holds and connects the processor to the system.
It ensures proper alignment and electrical contact between the CPU and motherboard.
🔌 What Is the Full Form of SATA?
SATA stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment.
It’s a standard interface used to connect storage devices like hard drives and SSDs to the motherboard.
🔄 What Connects to the Southbridge?
The southbridge connects to various peripheral devices and interfaces, including:
- USB ports
- Audio ports
- Serial and parallel ports
- SATA connectors for storage devices
- PCI slots for expansion cards
🧠 What Is a Motherboard Chipset?
A motherboard chipset is a collection of integrated circuits that manage data flow between the processor, memory, and peripherals.
It determines system compatibility and performance features.
🔌 What Is a PCI Slot?
A PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slot is an interface on the motherboard that allows expansion cards, such as graphics cards, network cards, and sound cards, to be added to the system.
🔌 What Is an M.2 Slot?
An M.2 slot is a connector on the motherboard designed for high-speed storage devices like SSDs.
It offers faster data transfer rates compared to traditional SATA connections.
🔄 What Is a Bus in a Computer?
A bus in a computer is a communication system that transfers data between components.
It includes data lines, address lines, and control lines, enabling efficient data exchange.
⚡ What Is PCIe?
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a high-speed interface standard used to connect expansion cards, such as GPUs and network cards, to the motherboard.
It offers faster data transfer rates compared to older PCI standards.
🔌 What Is a SATA Port?
A SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) port is a connector on the motherboard used to connect storage devices like hard drives and SSDs.
It supports data transfer between the storage device and the system.
⏰ What Is Power On by RTC?
Power On by RTC (Real-Time Clock) is a feature that allows the computer to automatically power on at a specified time, even if it was previously turned off.
⚡ What Is NVMe?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high-speed storage protocol designed for SSDs.
It offers faster data transfer rates and lower latency compared to traditional storage protocols.
🧠 What Is NAND?
NAND is a type of flash memory used in storage devices like SSDs.
It stores data in a non-volatile manner, meaning data is retained even when power is lost.
📦 What Is the Full Form of DDR?
DDR stands for Double Data Rate.
It’s a type of memory technology used in RAM modules, allowing for faster data transfer by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal.
💽 What Are the Three Types of SSDs?
The three main types of SSDs are:
- SATA SSDs: Use the SATA interface, offering moderate speed improvements over HDDs.
- NVMe SSDs: Connect via PCIe slots, providing significantly faster data transfer rates.
- M.2 SSDs: Compact form factor SSDs that can use either SATA or NVMe interfaces.
🧠 What Are E3 Drives?
E3 drives refer to SSDs designed for enterprise environments, offering higher endurance and reliability compared to consumer-grade SSDs.
💾 What Is SATA HDD?
A SATA HDD (Hard Disk Drive) is a traditional storage device that uses spinning disks to store data.
It connects to the motherboard via the SATA interface.
🚀 Which SSD Type Is Fastest?
NVMe SSDs are the fastest type of SSDs, offering superior data transfer speeds compared to SATA and M.2 SSDs.
🧠 How Many SSDs Can a PC Have?
The number of SSDs a PC can have depends on the motherboard’s available slots and connectors.
Modern motherboards often support multiple SSDs.
🔑 What Are the Different Types of SSD Keys?
SSD keys refer to the physical connectors on M.2 SSDs.
Common key types include:
- M-Key: Supports NVMe SSDs.
- B-Key: Supports SATA and PCIe x2 SSDs.
- M+B-Key: Compatible with both M and B keyed slots.
🔥 What Is the Heatsink on SSD?
A heatsink on an SSD is a thermal solution designed to dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing thermal throttling and ensuring optimal performance.
🔧 What Does an SSD Heatsink Look Like?
An SSD heatsink typically appears as a metal plate or finned structure attached to the SSD, aiding in heat dissipation.
🔩 Do SSDs Come with Screws?
Some SSDs come with screws for installation, while others may require separate purchase of mounting hardware.
🌡️ How to Check SSD Temperature?
You can check SSD temperature using software tools like CrystalDiskInfo or HWMonitor, which provide real-time temperature readings.
🧪 How to Check SSD Health?
SSD health can be monitored using tools like CrystalDiskInfo or the manufacturer’s proprietary software, which provide information on wear level, temperature, and error rates.
🧊 How Do I Check CPU Heat on Windows 11?
Windows 11 doesn’t have built-in tools for monitoring CPU temperature.
You can use third-party software like Core Temp or HWMonitor to check CPU temperature.
🌡️ How Hot Is an SSD?
SSDs typically operate within a temperature range of 0°C to 70°C.
Exceeding this range can lead to thermal throttling or potential damage.
🌡️ What Is the Temperature Range for Sandisk SSD?
The normal operating temperature for SanDisk SSDs is usually 0°C to 70°C, similar to most consumer SSDs.
🌡️ What Is a Normal GPU Temperature?
A normal GPU temperature while gaming is typically between 65°C and 85°C.
For idle use, it should remain between 30°C and 50°C.
🔥 What Part of the SSD Gets Hot?
The NAND chips and controller on an SSD are the main parts that generate heat.
The controller, in particular, can run significantly hotter than the NAND.
🌡️ What Is Thermal Throttling of External SSD?
Thermal throttling occurs when an external SSD gets too hot.
The SSD automatically reduces its speed to prevent overheating, leading to slower performance.
🌡️ What Is the Temperature of SSD NAND?
SSD NAND typically operates best between 0°C and 70°C.
Beyond this, data integrity and performance can be affected.
🐢 Do SSDs Slow Down When Hot?
Yes, SSDs can slow down when they overheat due to thermal throttling.
This protects the hardware but results in reduced performance.
🐌 Why Is SSD Getting Slower?
Reasons why an SSD may slow down include:
- Overheating
- Nearly full storage capacity
- Lack of TRIM command support
- Old firmware
- Too many write/erase cycles
❄️ How to Avoid SSD Overheating?
Ways to prevent SSD overheating:
- Use a heatsink or thermal pad
- Ensure proper airflow in the case
- Avoid enclosing the SSD in tight, unventilated areas
- Keep firmware updated
🥶 Can SSDs Get Cold?
Yes, SSDs can get cold. Most can operate in temperatures as low as 0°C (some industrial SSDs even lower).
However, extreme cold may affect performance until the drive warms up.
⏳ How Long Do SSDs Survive?
Consumer SSDs typically last 5 to 10 years, depending on usage.
Enterprise SSDs last longer due to higher endurance ratings.
💧 Can an SSD Get Wet?
No, SSDs are not waterproof.
If exposed to water, the circuitry can short out and become permanently damaged.
🌡️ What Is the Normal Temperature for NVMe Drive?
The normal operating temperature for an NVMe SSD is 30°C to 70°C.
Under heavy load, it may temporarily reach up to 80°C.
🔥 Why Does NVMe Get So Hot?
NVMe SSDs get hotter than SATA SSDs because they use PCIe lanes, which allow much higher data transfer speeds and therefore generate more heat.
🌡️ What Is the Maximum Temperature for SSD?
Most SSDs have a maximum safe temperature of 70°C to 85°C.
Exceeding this can lead to thermal throttling or permanent damage.
🆒 Do NVMe Drives Need Active Cooling?
While not always required, NVMe drives benefit from active cooling (like a fan or heatsink).
This helps prevent throttling during prolonged heavy workloads.
❄️ How Does an SSD Heatsink Work?
An SSD heatsink absorbs and spreads heat away from the SSD’s controller and NAND chips.
It helps maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevents throttling.
🖥️ What Are the Advantages of NVMe Drives?
Advantages of NVMe drives include:
- Much faster read/write speeds than SATA SSDs
- Lower latency
- Better parallelism (multiple tasks at once)
- Efficient use of PCIe lanes
💻 How to Keep NVMe Cool in Laptop?
Ways to keep an NVMe SSD cool in a laptop:
- Use a laptop cooling pad
- Ensure laptop vents are not blocked
- Undervolting/limiting SSD workload
- Some laptops support SSD heatsinks or thermal pads
🩹 How to Apply a Thermal Pad on SSD?
- Cut the thermal pad to the correct size.
- Place it gently on top of the SSD controller and NAND chips.
- Reattach the heatsink or cover so the pad makes contact with both surfaces.
🚀 How to Increase NVMe Speed?
- Enable X4 PCIe lanes in BIOS.
- Use latest NVMe drivers and firmware.
- Enable write caching in Windows.
- Keep SSD at least 20–30% free.
- Ensure thermal throttling is not limiting speed.
🔩 Do I Have to Screw in My M.2 SSD?
Yes, M.2 SSDs typically require a small screw to secure them to the motherboard.
This prevents them from moving or disconnecting.
🔩 What Uses M.2 Screws?
M.2 screws are specifically used to mount M.2 SSDs on a motherboard.
They are very small (often M2 x 3mm in size).
↕️ Which Way to Install M.2 SSD?
Align the notch (key) on the SSD with the M.2 slot on the motherboard.
Insert it at about a 30° angle, then push it down and secure it with a screw.
❓ Why Is My M.2 SSD Not Showing Up?
Possible reasons:
- SSD not properly seated
- BIOS not detecting the drive
- Drive not initialized or formatted
- Incompatible slot (NVMe vs SATA)
🪟 Why Is My M.2 Drive Not Showing Up in Windows Explorer?
If detected in BIOS but not Explorer:
- The SSD may not be partitioned.
- You need to initialize and format it via Disk Management in Windows.
📂 How Do I Partition a Hard Drive?
- Open Disk Management in Windows.
- Right-click the unallocated space and choose New Simple Volume.
- Assign a letter and format it (usually NTFS).
- Complete the setup, and the partition is ready.
⚡ What Is NVMe RAID Mode?
NVMe RAID mode allows you to combine multiple NVMe SSDs into a RAID array (RAID 0, 1, 5, etc.).
This provides benefits such as higher speed (RAID 0) or data redundancy (RAID 1).
Thanks For Learning !
Keep visiting keep learning


Leave a comment